These Are The US Banks With The Most Uninsured Deposits

Zero Hedge
This dollar value is roughly three times that of Apple's market capitalization, or about equal to 30% of U.S. GDP. Uninsured deposits are ones that exceed the $250,000 limit insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), which was actually increased from $100,000 after the Global Financial Crisis. They account for roughly 40% of all bank deposits.
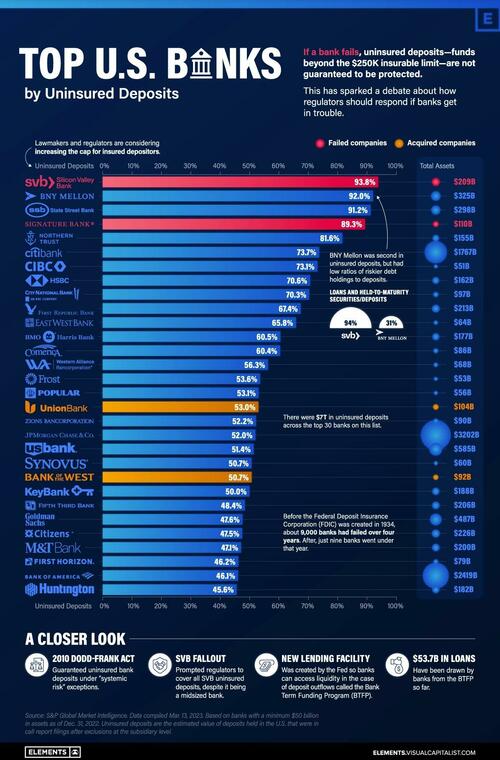
In the wake of the Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) fallout, Visual Capitalist's Dorothy Neufeld and Sabrina Lam look at the 30 U.S. banks with the highest percentage of uninsured deposits, using data from S&P Global.
Over the last month, SVB and Signature Bank went under at lightning speed.
Below, we show how their level of uninsured deposits compare to other banks. The dataset includes U.S. banks with at least $50 billion in assets at the end of 2022.
Bank of New York (BNY) Mellon and State Street Bank are the active banks with the highest levels of uninsured deposits. They are the two largest custodian banks in the U.S., followed by JP Morgan. Custodian banks provide critical infrastructure in the financial system, holding assets for safe-keeping for investment managers and transferring assets, among other duties.
Both BNY Mellon and State Street are considered “systemically important” banks.
Where these banks differ from SVB is that their loans and held-to-maturity securities as a percentage of total deposits are much lower. While these loans made up over 94% of SVB’s deposits, they made up 31% of BNY Mellon’s and 40% of State Street Bank’s deposits, respectively.
Held-to-maturity securities pose a greater risk to banks. Many of these holdings have lost value since interest rates have risen at a sharp clip. This presents interest-rate risks to banks. Consider how the value of long-term U.S. Treasurys declined about 30% in 2022. In this way, if a bank sells these assets before they mature, they take on a steep loss.
Overall, 11 banks on this list have loans and held-to-maturity assets that are over 90% of their total value of deposits.
Backstop Measures
To prevent wider ramifications, regulators implemented emergency actions. This was done by protecting all deposits of SVB and Signature Bank days after they announced failure.
The Fed also set up an emergency lending facility for banks. This Bank Term Funding Program (BTFP) was created to provide additional funding for banks if depositors pulled their money. It was also set up to prevent banks from interest-rate risk.
So far, more than $50 billion in loans have been withdrawn from the BTFP, up from $11.9 billion in its first week. (The Federal Reserve updates these numbers on a weekly basis.) This has led the Fed’s balance sheet to once again tick higher after slowly declining with the introduction of quantitative tightening in 2022.